Data
Data are simply values,
fact or set of values. It is represented in the form of text or number or in
the form of figures, tables, graphs, pictures etc. Data can be stored in
physical devices such as a memory.
Information
Meaningful or processed
data is called information. Example- student’s details, payroll system,
employee’s salary details, school- college information etc.
Data Structure
The data structure is an
organized collection of data. It is defined as a logical or mathematical model
of a particular organization of data. Abstract data type refers to the basic
mathematical concepts that define the data types such as Int, Float Character
etc.
The data structure also
provides a method of representing logical relationships between individual data
elements. It provides a convenient method to handle various data types
including Abstract Data Type (ADT). Example- Arrays, Linked List, Trees,
Stacks, Queues, Graphs etc.
Data structure performs
various operations to perform these data and also storing data to memory and
retrieving data from memory.
Study of Data Structure
The study of data structure
includes the following three steps.
Logical or mathematical
description of the structure (Algorithm)
Implementation of the structure on a computer(Operation)
Quantitative analysis of
the structure which includes determining the amount of memory needed to store
the structure and the time required to process the structure (Time-
space-complexity)
Classification of data
structures
The data structure has
variables associated with one another depending on the data. Data structure
performed some basic operations.
- Organizing data
- Accessing data (Retrieving data
- Manipulating data for information
(processing data)
The classification of data
depends on above the operations these are as follows.
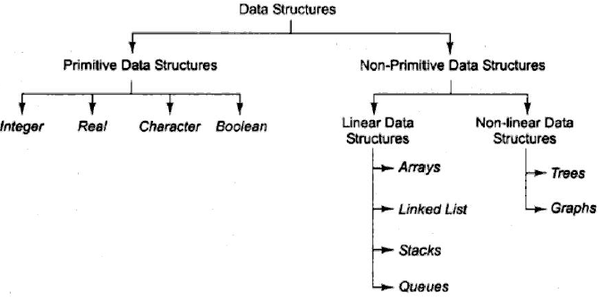
- Primitive data structures
- Non-Primitive data structures
 |
Classification of Data Structure
|
Primitive data structures
These structures which are
directly operated by machine level instructions and easily available in a
programming language. The memory representation for these type of structure are
predefined and the user can not change this. The storage structure of these
data structures vary from one machine to another. Examples of primitive data
structures are integer, float, character, double and pointer.
Non-Primitive Data
Structures
These structures are rarely
available in a programming language. They can not be operated by machine-level
instructions. The storage representation or memory representation is not
predefined. User has to define them i.e. user-defined structures. Examples of
non- primitive data structures are arrays, stacks, queues, files and linked
list.
Non-primitive data
structures are further classified into two types.
- Linear data
structures and
- Non-Linear data structure
Linear Data Structures
A data structure is said to
be linear if its elements form a sequence, or a linear list (the group of adjacent
data). This property is called as adjacency between the elements. Examples of
linear data structures are arrays, stacks, linked lists and queues.
Array: An array is a finite
set of homogeneous elements stored in adjacent memory locations. It is represented
by a single name with its index. The first element is num[0], the second
element is num[1] and so on. The last element is num[N-1], Here in fig. num[4].
 |
Structure of Array
|
Linked list: A linked list
is a linear collection of data items called nodes. Each node is divided into
two parts Information field and Link field. Each
node has an information field and a pointer, pointing to the next node of the
list called the linked field. It starts with a HEAD pointer, which stores the
pointer value of first node. The first node points to the second node and so
on. The last node does not point to anything, so it is indicated as a NULL
pointer.
 |
Link list
|
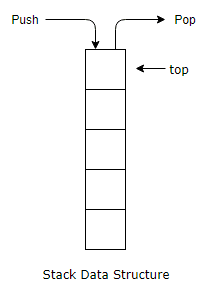
Stack: Stack is a linear
data structure in which data is inserted called push and deleted means pop at one end called top of
the stack. Here data are stored in the Last-In-First-Out manner.
 |
Stack of data structure
|
Queue: Queue is a linear the data structure in which data items can be inserted from one end called
the REAR and the data items can be deleted from the other end
called the FRONT.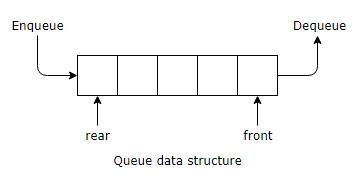 |
Queue in Data Structure
|
Non-Linear Data Structures
The data structures in
which data items are not arranged in order are called Non-linear data
structures. They may exhibit either a hierarchical relationship or a
parent-child relationship. Example- Trees and Graphs.
Trees: A Tree is a
recursive data structure containing the set of one or more data nodes where one
node is designated as the root of the tree while the remaining nodes are called
as the children of the root. They are maintaining either a parent-child
relationship between them or they are sister nodes. In general, the tree has
any number of children nodes but it can have only a single parent.
 |
Tree in Data Structure
|
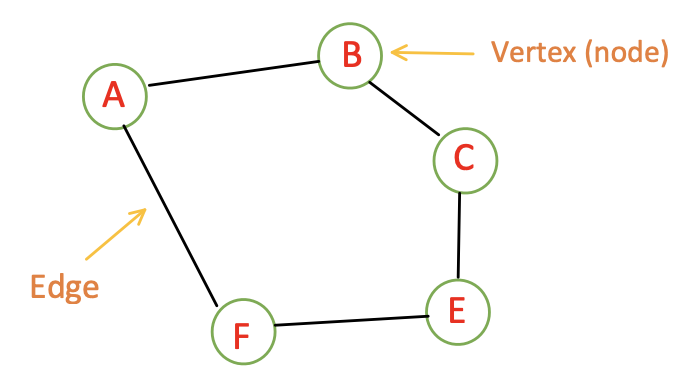
Graphs: A graph is a pictorial
representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by
links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed
as vertices, and the links that connect the vertices are
called edges.
 |
The graph in Data Structure
|







Comments
Post a Comment
Your comment will inspire me, Please leave your comment